Breast Reduction Female
Breast Reduction Female Procedures
IF YOU ARE CONSIDERING BREAST REDUCTION…
Women with very large, pendulous breasts may experience a variety of medical problems caused by the excessive weight, from back and neck pain and skin irritation to skeletal deformities and breathing problems. Bra straps may leave indentations in their shoulders. And unusually large breasts can make a woman (or a teenage girl) feel extremely self-conscious.
Breast reduction, technically known as reduction mammoplasty, is designed for such women. The procedure removes fat, glandular tissue, and skin from the breasts, making them smaller, lighter, and firmer. It can also reduce the size of the areola, the darker skin surrounding the nipple. The goal is to give the woman smaller, better-shaped breasts in proportion with the rest of her body.
If you’re considering breast reduction, this will give you a basic understanding of the procedure- when it can help, how it’s performed, and what results you can expect. It can’t answer all of your questions, since a lot depends on your individual circumstances. Please be sure to ask your doctor if there is anything about the procedure you don’t understand.
THE BEST CANDIDATES FOR BREAST REDUCTION
Breast reduction is usually performed for physical relief rather than simply cosmetic improvement. Most women who have the surgery are troubled by very large, sagging breasts that restrict their activities and cause them physical discomfort.
In most cases, breast reduction isn’t performed until a woman’s breasts are fully developed; however, it can be done earlier if large breasts are causing serious physical discomfort. The best candidates are those who are mature enough to fully understand the procedure and have realistic expectations about the results. Breast reduction is not recommended for women who intend to breast-feed.
ALL SURGERY CARRIES SOME UNCERTAINTY AND RISK
Breast reduction is not a simple operation, but it’s normally safe when performed by a qualified plastic surgeon. Nevertheless, as with any surgery, there is always a possibility of complications, including bleeding, infection, or reaction to the anesthesia. Some patients develop small sores around their nipples after surgery; these can be treated with antibiotic creams. You can reduce your risks by closely following your physician’s advice both before and after surgery.
The procedure does leave noticeable, permanent scars, although they’ll be covered by your bra or bathing suit. (Poor healing and wider scars are more common in smokers.) The procedure can also leave you with slightly mismatched breasts or unevenly positioned nipples. Future breast-feeding may not be possible, since the surgery removes many of the milk ducts leading to the nipples.
Some patients may experience a permanent loss of feeling in their nipples or breasts. Rarely, the nipple and areola may lose their blood supply and the tissue will die. (The nipple and areola can usually be rebuilt, however, using skin grafts from elsewhere on the body.)
PLANNING YOUR SURGERY
In your initial consultation, it’s important to discuss your expectations frankly with your surgeon, and to listen to his or her opinion. Every patient-and every physician, as well-has a different view of what is a desirable size and shape for breasts.
The surgeon will examine and measure your breasts, and will probably photograph them for reference during surgery and afterwards. (The photographs may also be used in the processing of your insurance coverage.) He or she will discuss the variables that may affect the procedure-such as your age, the size and shape of your breasts, and the condition of your skin. You should also discuss where the nipple and areola will be positioned; they’ll be moved higher during the procedure, and should be approximately even with the crease beneath your breasts.
Your surgeon should describe the procedure in detail, explaining its risks and limitations and making sure you understand the scarring that will result. The surgeon should also explain the anesthesia he or she will use, the facility where the surgery will be performed, and the costs. (Some insurance companies will pay for breast reduction if it’s medically necessary; however, they may require that a certain amount of breast tissue be removed. Check your policy, and have your surgeon write a “predetermination letter” if required.)
PREPARING FOR YOUR SURGERY
Your surgeon may require you to have a mammogram (breast x-ray) before surgery. You’ll also get specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery, including guidelines on eating and drinking, smoking, and taking or avoiding certain vitamins and medications. Some surgeons suggest that their patients diet before the operation.
Breast reduction doesn’t usually require a blood transfusion. However, if a large amount of breast tissue will be removed, your physician may advise you to have a unit of blood drawn ahead of time. That way, if a transfusion should be needed, your own blood can be used.
While you’re making preparations, be sure to arrange for someone to drive you home after your surgery and to help you out for a few days if needed.
WHERE YOUR SURGERY WILL BE PERFORMED
Breast reduction surgery may be performed in a hospital, an outpatient surgery center or an office-based surgical suite. If you are admitted to the hospital, your stay will be a short one. The surgery itself usually takes two to four hours, but may take longer in some cases.
TYPE OF ANESTHESIA
Breast reduction is nearly always performed under general anesthesia. You’ll be asleep through the entire operation.
THE SURGERY
Techniques for breast reduction vary, but the most common procedure involves an anchor-shaped incision that circles the areola, extends downward, and follows the natural curve of the crease beneath the breast. The surgeon removes excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin, and moves the nipple and areola into their new position. He or she then brings the skin from both sides of the breast down and around the areola, shaping the new contour of the breast. Liposuction may be used to remove excess fat from the armpit area.
In most cases, the nipples remain attached to their blood vessels and nerves. However, if the breasts are very large or pendulous, the nipples and areolas may have to be completely removed and grafted into a higher position. (This will result in a loss of sensation in the nipple and areolar tissue.)
Stitches are usually located around the areola, in a vertical line extending downward, and along the lower crease of the breast. In some cases, techniques can be used that eliminate the vertical part of the scar. And occasionally, when only fat needs to be removed, liposuction alone can be used to reduce breast size, leaving minimal scars.
AFTER YOUR SURGERY
After surgery, you’ll be wrapped in an elastic bandage or a surgical bra over gauze dressings. A small tube may be placed in each breast to drain off blood and fluids for the first day or two.
You may feel some pain for the first couple of days -especially when you move around or cough- and some discomfort for a week or more. Your surgeon will prescribe medication to lessen the pain.
The bandages will be removed a day or two after surgery, though you’ll continue wearing the surgical bra around the clock for several weeks, until the swelling and bruising subside. Your stitches will be removed in one to three weeks.
If your breast skin is very dry following surgery, you can apply a moisturizer several times a day, but be sure to keep the suture area dry.
Your first menstruation following surgery may cause your breasts to swell and hurt. You may also experience random, shooting pains for a few months. You can expect some loss of feeling in your nipples and breast skin, caused by the swelling after surgery. This usually fades over the next six weeks or so. In some patients, however, it may last a year or more, and occasionally it may be permanent.
GETTING BACK TO NORMAL
Although you may be up and about in a day or two, your breasts may still ache occasionally for a couple of weeks. You should avoid lifting or pushing anything heavy for three or four weeks.
Your surgeon will give you detailed instructions for resuming your normal activities. Most women can return to work (if it’s not too strenuous) and social activities in about two weeks. But you’ll have much less stamina for several weeks, and should limit your exercises to stretching, bending, and swimming until your energy level returns. You’ll also need a good athletic bra for support.
You may be instructed to avoid sex for a week or more, since sexual arousal can cause your incisions to swell, and to avoid anything but gentle contact with your breasts for about six weeks.
A small amount of fluid draining from your surgical wound, or some crusting, is normal. If you have any unusual symptoms, such as bleeding or severe pain, don’t hesitate to call your doctor.
YOUR NEW LOOK
Although much of the swelling and bruising will disappear in the first few weeks, it may be six months to a year before your breasts settle into their new shape. Even then, their shape may fluctuate in response to your hormonal shifts, weight changes, and pregnancy.
Your surgeon will make every effort to make your scars as inconspicuous as possible. Still, it’s important to remember that breast reduction scars are extensive and permanent. They often remain lumpy and red for months, then gradually become less obvious, sometimes eventually fading to thin white lines. Fortunately, the scars can usually be placed so that you can wear even low-cut tops.
Of all plastic surgery procedures, breast reduction results in the quickest body-image changes. You’ll be rid of the physical discomfort of large breasts, your body will look better proportioned, and clothes will fit you better.
However, as much as you may have desired these changes, you’ll need time to adjust to your new image-as will your family and friends. Be patient with yourself, and with them. Keep in mind why you had this surgery, and chances are that, like most women, you’ll be pleased with the results.

Heavy breasts can lead to physical discomfort, a variety of medical problems, shoulder indentations due to tight bra straps, and extreme self-consciousness.
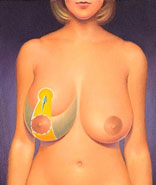
Incisions outline the area of skin, breast tissue, and fat to be removed and the new position for the nipple.

Skin formerly located above the nipple is brought down and together to reshape the breast. Sutures close the incisions, giving the breast it’s new contour.
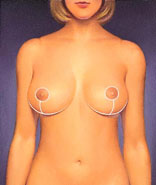
Scars around the areola, below it, and in the crease under the breast are permanent, but can be easily concealed by clothing.
With smaller, better proportioned breasts, you’ll feel more comfortable and your clothes will fit better.
Breast
Breast Reduction Female Procedures

Heavy breasts can lead to physical discomfort, a variety of medical problems, shoulder indentations due to tight bra straps, and extreme self-consciousness.

Incisions outline the area of skin, breast tissue, and fat to be removed and the new position for the nipple.

Skin formerly located above the nipple is brought down and together to reshape the breast. Sutures close the incisions, giving the breast it’s new contour.

Scars around the areola, below it, and in the crease under the breast are permanent, but can be easily concealed by clothing.

With smaller, better proportioned breasts, you’ll feel more comfortable and your clothes will fit better.
IF YOU ARE CONSIDERING BREAST REDUCTION…
Women with very large, pendulous breasts may experience a variety of medical problems caused by the excessive weight, from back and neck pain and skin irritation to skeletal deformities and breathing problems. Bra straps may leave indentations in their shoulders. And unusually large breasts can make a woman (or a teenage girl) feel extremely self-conscious.
Breast reduction, technically known as reduction mammoplasty, is designed for such women. The procedure removes fat, glandular tissue, and skin from the breasts, making them smaller, lighter, and firmer. It can also reduce the size of the areola, the darker skin surrounding the nipple. The goal is to give the woman smaller, better-shaped breasts in proportion with the rest of her body.
If you’re considering breast reduction, this will give you a basic understanding of the procedure- when it can help, how it’s performed, and what results you can expect. It can’t answer all of your questions, since a lot depends on your individual circumstances. Please be sure to ask your doctor if there is anything about the procedure you don’t understand.
THE BEST CANDIDATES FOR BREAST REDUCTION
Breast reduction is usually performed for physical relief rather than simply cosmetic improvement. Most women who have the surgery are troubled by very large, sagging breasts that restrict their activities and cause them physical discomfort.
In most cases, breast reduction isn’t performed until a woman’s breasts are fully developed; however, it can be done earlier if large breasts are causing serious physical discomfort. The best candidates are those who are mature enough to fully understand the procedure and have realistic expectations about the results. Breast reduction is not recommended for women who intend to breast-feed.
ALL SURGERY CARRIES SOME UNCERTAINTY AND RISK
Breast reduction is not a simple operation, but it’s normally safe when performed by a qualified plastic surgeon. Nevertheless, as with any surgery, there is always a possibility of complications, including bleeding, infection, or reaction to the anesthesia. Some patients develop small sores around their nipples after surgery; these can be treated with antibiotic creams. You can reduce your risks by closely following your physician’s advice both before and after surgery.
The procedure does leave noticeable, permanent scars, although they’ll be covered by your bra or bathing suit. (Poor healing and wider scars are more common in smokers.) The procedure can also leave you with slightly mismatched breasts or unevenly positioned nipples. Future breast-feeding may not be possible, since the surgery removes many of the milk ducts leading to the nipples.
Some patients may experience a permanent loss of feeling in their nipples or breasts. Rarely, the nipple and areola may lose their blood supply and the tissue will die. (The nipple and areola can usually be rebuilt, however, using skin grafts from elsewhere on the body.)
PLANNING YOUR SURGERY
In your initial consultation, it’s important to discuss your expectations frankly with your surgeon, and to listen to his or her opinion. Every patient-and every physician, as well-has a different view of what is a desirable size and shape for breasts.
The surgeon will examine and measure your breasts, and will probably photograph them for reference during surgery and afterwards. (The photographs may also be used in the processing of your insurance coverage.) He or she will discuss the variables that may affect the procedure-such as your age, the size and shape of your breasts, and the condition of your skin. You should also discuss where the nipple and areola will be positioned; they’ll be moved higher during the procedure, and should be approximately even with the crease beneath your breasts.
Your surgeon should describe the procedure in detail, explaining its risks and limitations and making sure you understand the scarring that will result. The surgeon should also explain the anesthesia he or she will use, the facility where the surgery will be performed, and the costs. (Some insurance companies will pay for breast reduction if it’s medically necessary; however, they may require that a certain amount of breast tissue be removed. Check your policy, and have your surgeon write a “predetermination letter” if required.)
PREPARING FOR YOUR SURGERY
Your surgeon may require you to have a mammogram (breast x-ray) before surgery. You’ll also get specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery, including guidelines on eating and drinking, smoking, and taking or avoiding certain vitamins and medications. Some surgeons suggest that their patients diet before the operation.
Breast reduction doesn’t usually require a blood transfusion. However, if a large amount of breast tissue will be removed, your physician may advise you to have a unit of blood drawn ahead of time. That way, if a transfusion should be needed, your own blood can be used.
While you’re making preparations, be sure to arrange for someone to drive you home after your surgery and to help you out for a few days if needed.
WHERE YOUR SURGERY WILL BE PERFORMED
Breast reduction surgery may be performed in a hospital, an outpatient surgery center or an office-based surgical suite. If you are admitted to the hospital, your stay will be a short one. The surgery itself usually takes two to four hours, but may take longer in some cases.
TYPE OF ANESTHESIA
Breast reduction is nearly always performed under general anesthesia. You’ll be asleep through the entire operation.
THE SURGERY
Techniques for breast reduction vary, but the most common procedure involves an anchor-shaped incision that circles the areola, extends downward, and follows the natural curve of the crease beneath the breast. The surgeon removes excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin, and moves the nipple and areola into their new position. He or she then brings the skin from both sides of the breast down and around the areola, shaping the new contour of the breast. Liposuction may be used to remove excess fat from the armpit area.
In most cases, the nipples remain attached to their blood vessels and nerves. However, if the breasts are very large or pendulous, the nipples and areolas may have to be completely removed and grafted into a higher position. (This will result in a loss of sensation in the nipple and areolar tissue.)
Stitches are usually located around the areola, in a vertical line extending downward, and along the lower crease of the breast. In some cases, techniques can be used that eliminate the vertical part of the scar. And occasionally, when only fat needs to be removed, liposuction alone can be used to reduce breast size, leaving minimal scars.
AFTER YOUR SURGERY
After surgery, you’ll be wrapped in an elastic bandage or a surgical bra over gauze dressings. A small tube may be placed in each breast to drain off blood and fluids for the first day or two.
You may feel some pain for the first couple of days -especially when you move around or cough- and some discomfort for a week or more. Your surgeon will prescribe medication to lessen the pain.
The bandages will be removed a day or two after surgery, though you’ll continue wearing the surgical bra around the clock for several weeks, until the swelling and bruising subside. Your stitches will be removed in one to three weeks.
If your breast skin is very dry following surgery, you can apply a moisturizer several times a day, but be sure to keep the suture area dry.
Your first menstruation following surgery may cause your breasts to swell and hurt. You may also experience random, shooting pains for a few months. You can expect some loss of feeling in your nipples and breast skin, caused by the swelling after surgery. This usually fades over the next six weeks or so. In some patients, however, it may last a year or more, and occasionally it may be permanent.
GETTING BACK TO NORMAL
Although you may be up and about in a day or two, your breasts may still ache occasionally for a couple of weeks. You should avoid lifting or pushing anything heavy for three or four weeks.
Your surgeon will give you detailed instructions for resuming your normal activities. Most women can return to work (if it’s not too strenuous) and social activities in about two weeks. But you’ll have much less stamina for several weeks, and should limit your exercises to stretching, bending, and swimming until your energy level returns. You’ll also need a good athletic bra for support.
You may be instructed to avoid sex for a week or more, since sexual arousal can cause your incisions to swell, and to avoid anything but gentle contact with your breasts for about six weeks.
A small amount of fluid draining from your surgical wound, or some crusting, is normal. If you have any unusual symptoms, such as bleeding or severe pain, don’t hesitate to call your doctor.
YOUR NEW LOOK
Although much of the swelling and bruising will disappear in the first few weeks, it may be six months to a year before your breasts settle into their new shape. Even then, their shape may fluctuate in response to your hormonal shifts, weight changes, and pregnancy.
Your surgeon will make every effort to make your scars as inconspicuous as possible. Still, it’s important to remember that breast reduction scars are extensive and permanent. They often remain lumpy and red for months, then gradually become less obvious, sometimes eventually fading to thin white lines. Fortunately, the scars can usually be placed so that you can wear even low-cut tops.
Of all plastic surgery procedures, breast reduction results in the quickest body-image changes. You’ll be rid of the physical discomfort of large breasts, your body will look better proportioned, and clothes will fit you better.
However, as much as you may have desired these changes, you’ll need time to adjust to your new image-as will your family and friends. Be patient with yourself, and with them. Keep in mind why you had this surgery, and chances are that, like most women, you’ll be pleased with the results.
